In biocontrol of the skin pathogens and analysis of their physiology we are focusing on the application of pulsed electric field (PEF) in combination with the various chemical compounds to achieve the successful elimination of the skin pathogens, both bacteria and yeasts. The skin pathogens, Candida genera yeast, are capable of undergoing morphology switches and form pseudohyphae structures with highly increased resistance to the antifungal compounds. We discovered that, after growth in a rotary cell cultivation system (RCCS), a new, super-resistant and morphology-switching-unrelated phenotype of Candida is formed [1]. RCCS is changing the pattern of the antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus as well. A combination of the novel chemical compounds with the pulsed electric field (PEF) and pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) technologies allows us to perform a wide scale biocontrol of the drug resistant skin pathogens [2].
In 2020, we started a new project “The influence of intensive fish farming on aquatic microbiome and resistome”, analysing and comparing the microbial communities in the fresh aquatic systems and fish farms. These studies provide information not only concerning the microbial communities present in the environmental samples, but also regarding the pathogens and antibiotic resistant strains that can be spread in the population. In this research, we are also focusing on the bacteria genotypes that could be related to the microplastic degradation, synthesis of the antimicrobial compounds, capability to grow on different carbon sources.
Protein engineering (directed evolution, rational design, enzyme fusion) is a powerful tool for developing new biocatalysts for different industrial fields. Lipolytic enzymes are extensively used in chemistry, food, pharmaceutical, detergent, cosmetics industry and biodiesel production. Our research team apply different protein engineering methods (random and site-specific mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, SHIPREC, epPCR, the design of new fused biocatalysts) to investigate structure-function relationships of lipolytic enzymes produced by Geobacillus bacteria. In our research, we predicted a few amino acids, which strongly affected the activity of these enzymes, constructed several fused lipolytic enzymes and developed new Geobacillus lipase variant with improved kinetics and physicochemical characteristics (4–6).
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS
1. Lastauskiene, E., Novickij, V., Zinkevičiene, A., Girkontaite, I., Paškevičius, A., Svediene, J., Markovskaja, S., Novickij, J. Application of pulsed electric fields for the elimination of highly drug-resistant Candida grown under modelled microgravity conditions. International Journal of Astrobiology. 2019, 18: 405–411.
2. Novickij, V., Staigvila, G., Gudiukaitė, R., Zinkevičienė, A., Girkontaitė, I., Paškevičius, A., Švedienė, J., Markovskaja, S., Novickij, J., Lastauskienė, E. Nanosecond duration pulsed electric field together with formic acid triggers caspase-dependent apoptosis in pathogenic yeasts. Bioelectrochemistry. 2019, 128: 148–154.
3. Novickij, V., Lastauskienė, E., Staigvila, G., Girkontaitė, I., Zinkevičienė, A., Švedienė, J., Paškevičius, A., Markovskaja, S., Novickij, J. Low concentrations of acetic and formic acids enhance the inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with pulsed electric fields. BMC Microbiology. 2019, 19: 73.
4. Druteika, G., Sadauskas, M., Malunavicius, V., Lastauskiene, E., Statkeviciute, R., Savickaite, A., Gudiukaite, R. New engineered Geobacillus lipase GD-95RM for industry focusing on the cleaner production of fatty esters and household washing product formulations. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2020, 36: 41. doi: 10.1007/s11274-020-02816-3.
5. Kumar, A., Gudiukaite, R., Gricajeva, A., Sadauskas, M., Malunavicius, V., Kamyab, H., Sharma, S., Sharma, T., Pant, D. Microbial lipolytic enzymes – promising energy-efficient biocatalysts in bioremediation. Energy. 2020, 192: 116674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116674.
6. Druteika, G., Sadauskas, M., Malunavicius, V., Lastauskiene, E., Taujenis, L., Gegeckas, A., Gudiukaitė, R. Development of a new Geobacillus lipase variant GDlip43 via directed evolution leading to identification of new activity-regulating amino acids. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020, 151: 1194–1204.
The Candida genera yeast-caused infections are frequent and difficult to treat, as the physiology and metabolisms of yeast are similar to the host [1]. Induction of the programmed cell death is of great medical relevance, since during apoptosis peptides, nucleotides, amino acids and other compounds are released to the surrounding media and can contribute to the regeneration of the human tissues. Discovery of the apoptogenic substances for the biocontrol of pathogenic yeasts as well as optimization of the apoptogenic conditions is the main task of our research group. PEF can be also successfully applied to inactivate bacterial pathogen colonizing human skin. Best results are achieved by combining PEF with the week organic acids [2, 3].
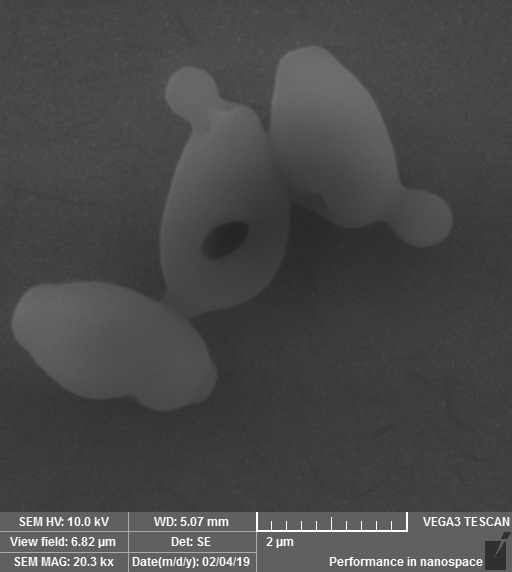

PEF treated yeast cells. Scanning electron microscopy.
The biodiversity of fishery ponds is changed towards fulfilling the industrial needs, therefore reducing the microbial biodiversity and precautions should be taken to keep the system sustainable and protect the adjacent environment from possible damage. The metagenome analysis allows us to assess prokaryotic diversity in aquatic environment and evaluate the influence of intensive fish farming on the environment. We aim to evaluate the current situation in the fishery ponds, fresh water environments and adjacent aqua systems in order to understand the microbial population dynamics.
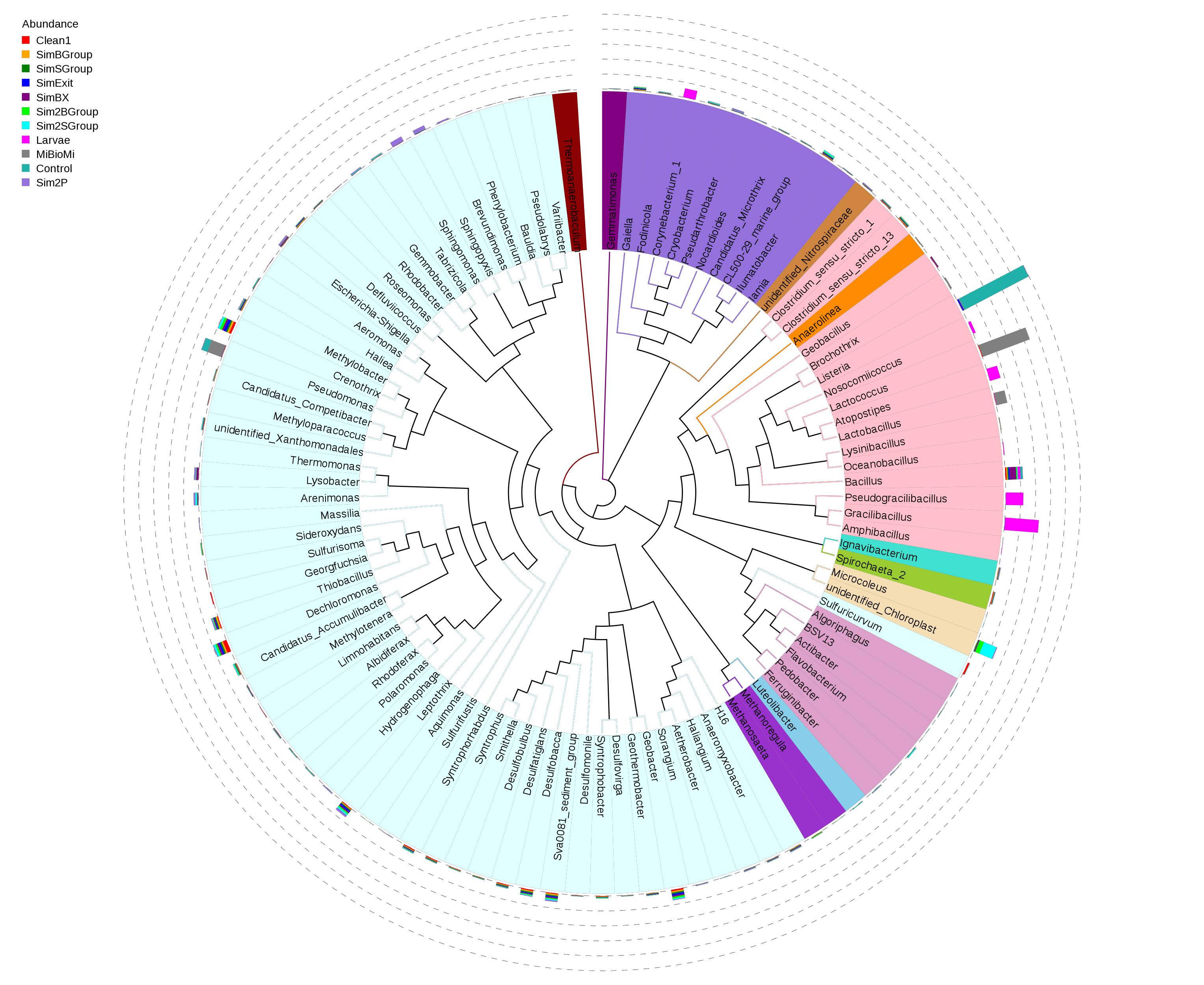
Bacterial genus diversity in the fish farm ponds.
Microbial lipolytic enzymes have gained attention for the ability to catalyse biotransformation reactions of different esters-bond containing compounds. Conversion of the latter into high-energy products like biofuel and other value-added products (fatty acid esters, mono- and diacylglycerols, etc.) in an energy-efficient and ecologically-friendly way makes these biocatalysts an important tool for sustainable biotechnology. Protein engineering, immobilization and application of Geobacillus lipases and carboxylesterases is one of the major research fields of our group [4–6].
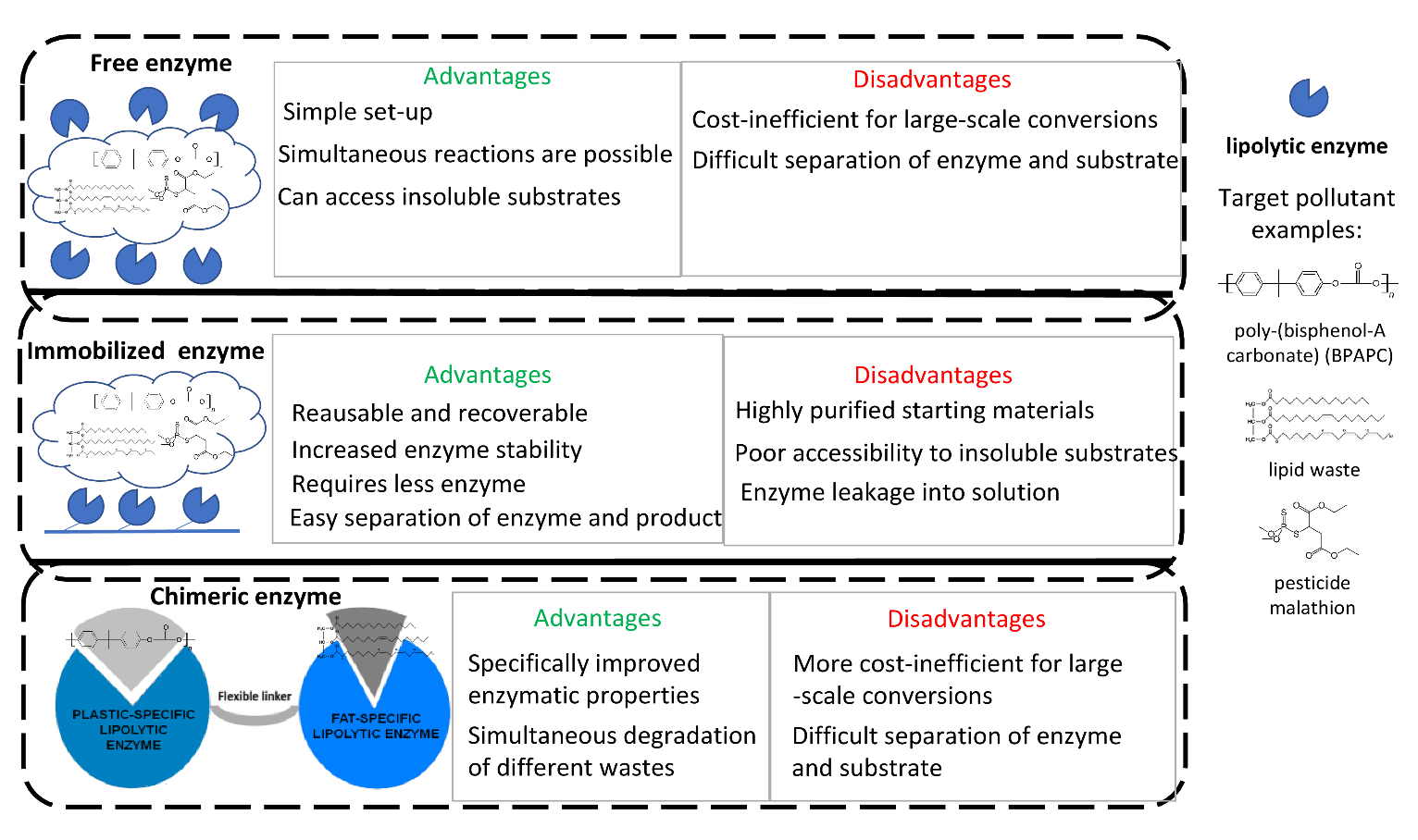
The main advantages and disadvantages of lipolytic microbial enzymes usage in immobilized, free and chimeric forms [5].
Microbially induced calcite precipitation (MICP) is an effective and eco-friendly technology that can be applied to solve soil problems, including soil erosion, pollution with heavy metals and radionuclides or for CO2 sequestration. In geotechnical engineering, bioconsolidation is an effective technique to increase slope stability. The success of this process depends on ureases producing microorganisms. We have shown that using both 0.5–1 M concentration of urea with CaCl2 and urease positive Staphylococcus sp. H6 cells successful MICP process can be carried out.
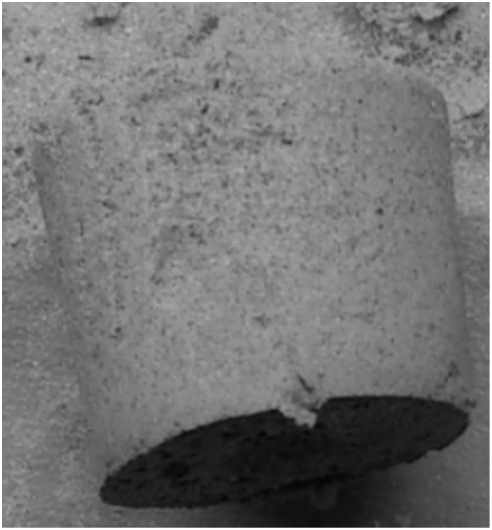

Bioconsolidated sand particles obtained during MICP using Staphylococcus sp. H6